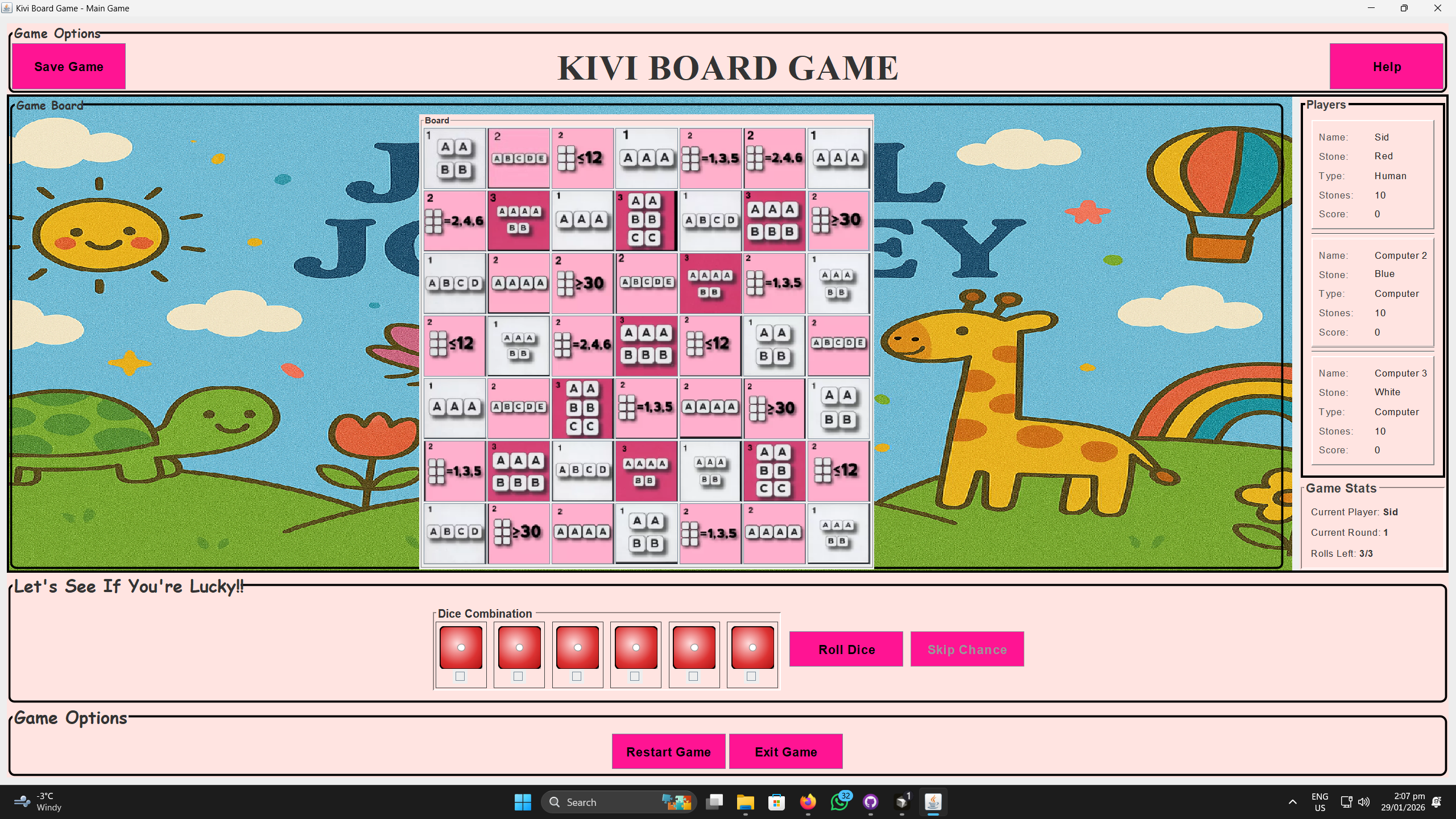
Project Overview
KiviBoardGame delivers a full Java Swing adaptation of the dice strategy board game Kivi: 2–4 players (human/AI) roll to match patterns on a 7×7 grid, build scoring lines over 10 rounds, with save/load and color vision support.
To run the game: Java installed (JDK/JRE 17+ recommended).
Tech Stack
Core Technical Stack
- Java
- Java Swing
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
- GRASP Design Patterns
- Multi-threading
- Java Serialization
Systems & Logic
- Game Architecture
- AI Heuristics & Logic
- Pattern Validation Algorithms
- State Management
- Concurrency Control
UI/UX & Accessibility
- Event-Driven Programming
- Inclusive Design (CVD Support)
- Interface Decoupling
- Asset Integration
Tools & Workflow
- GitHub
- IntelliJ IDEA
- Technical Documentation
- Figma
Features & Contributions
Setup & Main Menu
Configure 2–4 players: human/AI (Easy/Hard), names, colors, vision mode, and backgrounds via the MainMenu.
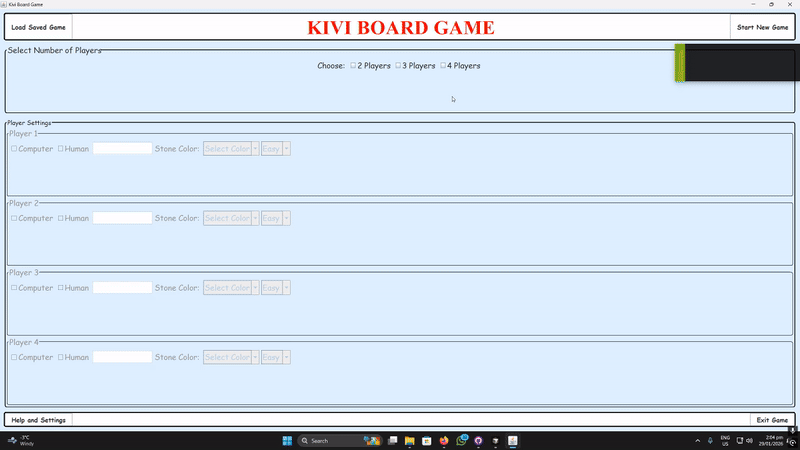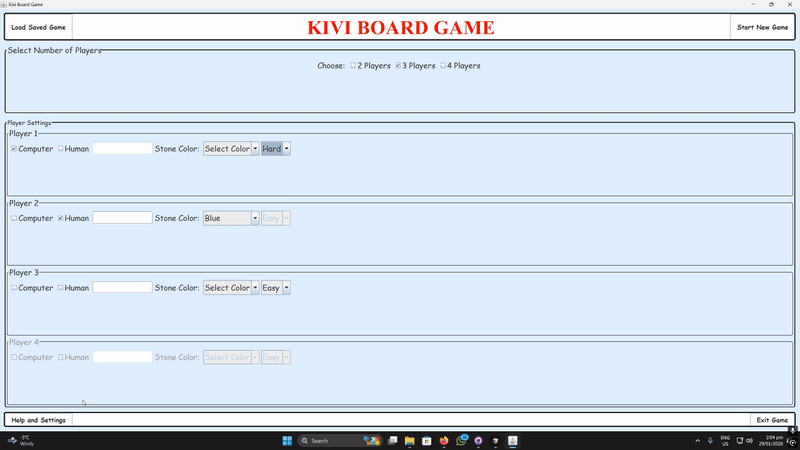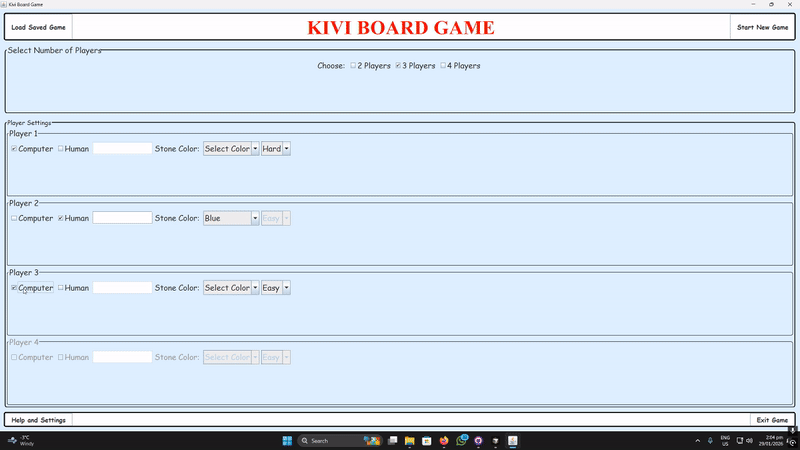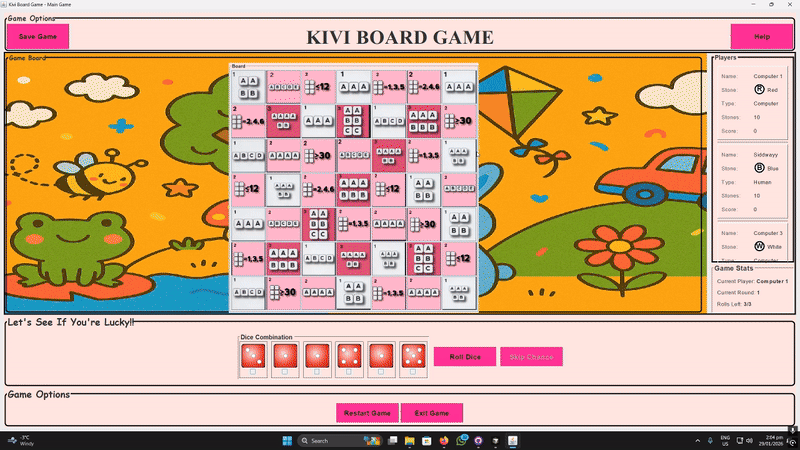
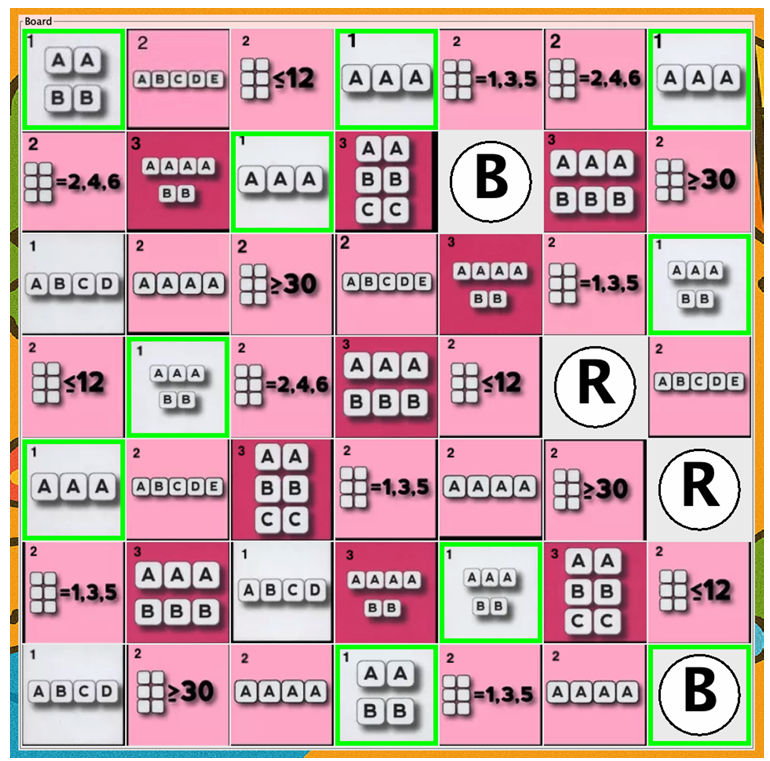
Core Gameplay Loop
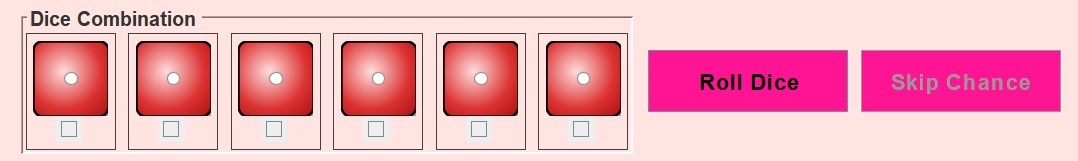
Roll 6 dice (up to 3 times) → grid highlights pattern matches → place stone → live stats update → next player. 10 rounds to win!
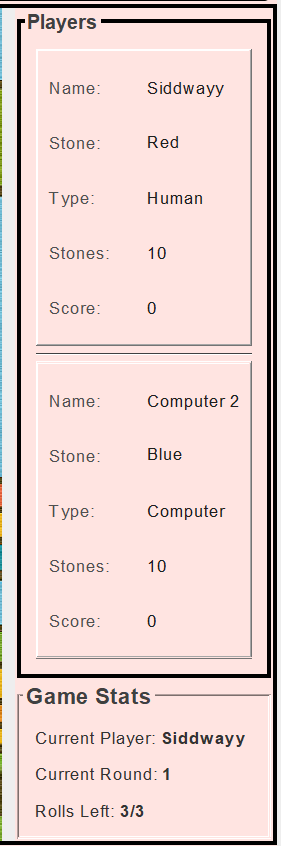
Player Stats & UI
Real-time panels show names, colors (R/G/B/W), stones left, and scores – only the current player can act.
Save/Load Feature
Serialize full game state (board, players, round) – pause and resume anytime.
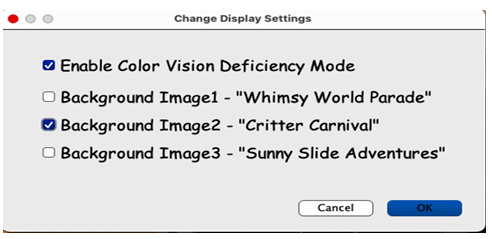
Accessibility Options
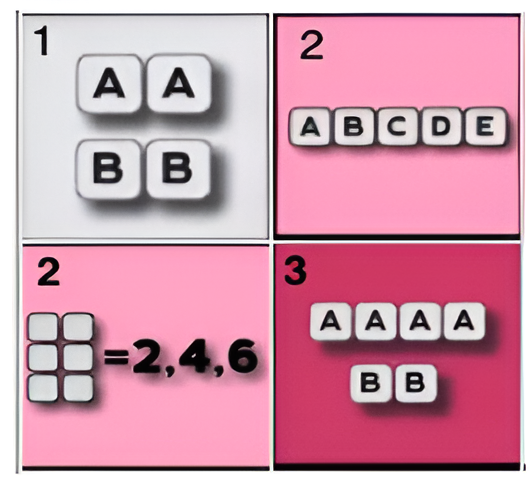
Toggle color vision deficiency mode (numbered grids 1–3, labeled stones) and custom backgrounds (Whimsy World, Critter Carnival).
Game Over & Win
Final scores are calculated; winner is announced with a Duke mascot popup.

Technical Implementation
Architecture & GRASP
The game is structured around a central GameManager that acts as the controller: it coordinates turns, validates moves, updates the board and scores, and notifies the UI. UI and logic stay decoupled via a GridCellClickListener so grid clicks are handled separately from game logic (low coupling). All dice-rule checks live in a single validateDiceCombination method so rule changes don’t ripple through the codebase (protected variations). The AI runs as a ComputerPlayerAI thread so the UI stays responsive during computer turns (pure fabrication).
Dice validation
A roll is valid if it matches one of three patterns: sum over 30, three pairs, or a straight 1–6. Validation is centralized: dice are sorted, then checked against each pattern. Only valid combinations allow placing a stone, and the grid highlights only cells that match the current roll.
Real-time grid highlighting
When the player rolls, the grid loops over all empty cells, checks whether the dice match each cell’s required pattern, and highlights valid cells (e.g. green border). Transient state like highlights is cleared and repainted each time. The logic is driven by the same validation used for placement, so the UI always reflects the current roll.
AI behavior
Easy AI rolls at most twice and picks a random valid placement. Hard AI gets three rolls and uses a prioritizeBlocking step to prefer moves that block the opponent’s longest line. All AI work runs on a background thread; when done, it calls SwingUtilities.invokeLater to update the GameManager and end the turn on the EDT.
Persistence
Save writes the full GameManager (board, players, round, state) plus current player index and game state to an ObjectOutputStream. Transient fields such as threads are not serialized. Load reads those objects back and then calls restoreUI to rebuild panels and state from the loaded model so the player can resume exactly where they left off.